Significant maintenance benefits at Year 1 that were maintained at Year 2 (open-label extension)2
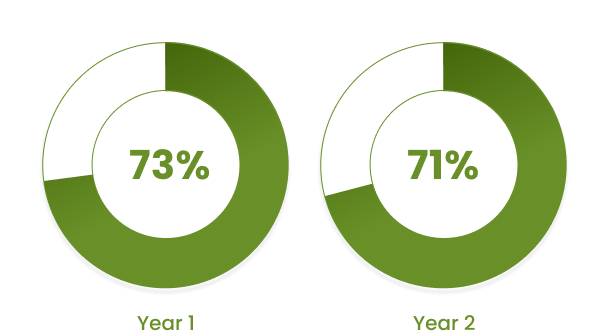
Patients with Crohn's disease achieving clinical remission at Years 1 and 2
Patients with ulcerative colitis achieving clinical remission at Years 1 and 2
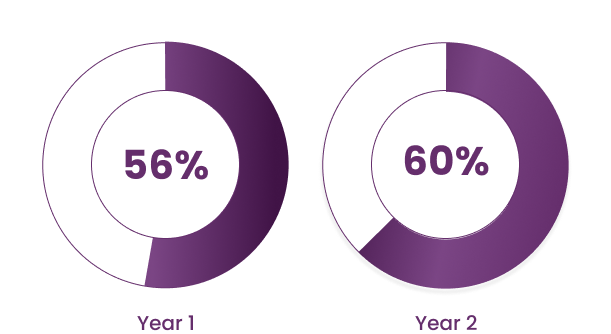
Study Note: Extension phases of randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD) (N=231 at Year 1; N=192 at Year 2) or ulcerative colitis (UC) (N=294 at Year 1; N=237 at Year 2). Patients who completed maintenance and were deemed by the investigator to benefit from continued treatment could join the open-label extension phase from Week 56 to Week 102, regardless of their previous maintenance arm. Efficacy endpoints for CD were clinical remission, endoscopic remission, endoscopic response, corticosteroid-free remission, CDAI-100 response, and deep remission. Efficacy endpoints for UC were clinical remission, histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement, and corticosteroid-free remission.2
Limitations: In an open-label extension, there is a potential for enrichment of the long-term data in the remaining patient populations, since patients who are unable to tolerate or do not respond to the drug often drop out. In the as-observed analysis, missing visit data were excluded, potentially increasing the percentage of responders.2
Explore the Data
Select the data you'd like to explore below
ZYMFENTRA maintenance therapy provided significant clinical benefits in patients with moderate to severe CD1
Primary and secondary endpoints for SC maintenance at Year 1
Study Note: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=323) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Co-primary endpoints were clinical remission and endoscopic response. Secondary endpoints were endoscopic remission and corticosteroid-free remission.1
Definition of endpoints: Clinical remission: Absolute CDAI score of <150 points. Endoscopic response: >50% decrease in SES-CD score from the baseline value. Endoscopic remission: SES-CD of ≤4 and at least a 2-point reduction from the baseline value with no segment sub-score of >1. Corticosteroid-free remission: Achieves clinical remission without corticosteroid use for at least 8 weeks prior to Week 54, among the patients who used oral corticosteroids at baseline.1
CD, Crohn's disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous; SES-CD, Simplified Endoscopic Activity Score for Crohn's Disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038
ZYMFENTRA maintenance therapy provided significant clinical benefits in patients with moderate to severe UC1
Primary and secondary endpoints for SC maintenance at Year 1
Study Note: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=438) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC. Primary endpoint was clinical remission. Secondary endpoints were histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement and corticosteroid-free remission.1
Definitions of endpoints: Clinical remission: Modified Mayo Score (mMS) with a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 point, rectal bleeding subscore of 0 point, and endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 point. Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement: Absolute endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 (excluding friability) from the mMS and an absolute Robarts Histopathology Index score of ≤3 points with no lamina propria neutrophils, no neutrophils in epithelium, no erosion or ulceration. Corticosteroid-free remission: Achieves clinical remission without corticosteroid use for at least 8 weeks prior to Week 54, among the patients who used oral corticosteroids at baseline.1
CD, Crohn's disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038
Durable remission at Year 2 in patients with UC and CD5*
-
Efficacy results with non-responder imputation for CD:
From Week 54 to Week 102, 81% of patients achieved durable remission5
-
Efficacy results with non-responder imputation for UC:
From Week 54 to Week 102, 69% of patients achieved durable remission5
Definition of endpoint: Clinical remission: Absolute CDAI score of <150 points.
*Durable remission at Week 102 (as-observed analysis): 88% of patients with CD and 84% with UC. Among patients in the open-label extension, the percentage of patients who achieved clinical remission at Week 54 and maintained clinical remission at Week 102.
After IFX IV induction, patients achieved clinical remission at Week 54 and maintained clinical remission at Week 102.2
LIBERTY CD trial 2-year open-label extension2,6
LIBERTY CD Trial: Week 102 extension-phase efficacy results as-observed analysis
Study Note: Extension phase of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=231 at Year 1; N=192 at Year 2) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Patients who completed maintenance and deemed by the investigator to benefit from continued treatment could join the open-label extension phase from Week 56 to Week 102, regardless of their previous maintenance arm. Co-primary endpoints were clinical remission and endoscopic response. Secondary endpoints were endoscopic remission, corticosteroid-free remission, CDAI-100 response, and deep remission.2,6
Definitions of endpoints: Clinical remission: Absolute CDAI score of ≤150 points. Endoscopic response: 50% decrease in SES-CD score from the baseline value. Endoscopic remission: SES-CD of ≤4 and at least a 2-point reduction from the baseline value with no subscore of >1. Corticosteroid-free remission: Achieves clinical remission without corticosteroid use for at least 8 weeks prior to Week 54 among the patients who used oral corticosteroids at baseline. CDAI-100 response: Decrease in CDAI score of 100 or more points from the baseline value. Deep remission: Composite of clinical remission and endoscopic remission.2
Efficacy results with non-responder imputation for CD: At Week 54, 73% of patients achieved clinical remission vs 64% at Week 102. Endoscopic response was achieved at Week 54 in 60% vs 49% at Week 102. Endoscopic remission was achieved in 41% at Week 54 vs 33% at Week 102. Corticosteroid-free remission was achieved at Week 54 in 51% vs 42% at Week 102.2,6
Limitations: In an open-label extension, there is a potential for enrichment of the long-term data in the remaining patient populations, since patients who are unable to tolerate or do not respond to the drug often drop out. In the as-observed analysis, missing visit data were excluded, potentially increasing the percentage of responders.2,6
CD, Crohn's Disease; CDAI, Crohn's disease Activity Index; IFX, infliximab; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous; SES-CD, Simplified Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038 5. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Supplementary material to: Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 6. Hanauer SB, Sand BE, Schreiber S, et al. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: two randomized phase 3 trials (LIBERTY). Gastroenterol. 2024;167(5):919-933. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.006
LIBERTY UC trial 2-year open-label extension2,6
LIBERTY UC Trial: Week 102 extension phase efficacy results as-observed analysis
Study Note: Extension phase of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=294 at Year 1; N=237 at Year 2) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC. Primary endpoint was clinical remission. Secondary endpoints were histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement and corticosteroid-free remission.2,6
Definitions of endpoints: Clinical remission: Modified Mayo Score (mMS) with a stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1 point, rectal bleeding subscore of 0 point, and endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 point. Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement: Absolute endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 (excluding friability) from the mMS and an absolute Robarts Histopathology Index score of ≤3 points with no lamina propria neutrophils, no neutrophils in epithelium, no erosion or ulceration. Corticosteroid-free remission: Achieves clinical remission without corticosteroid use for at least 8 weeks prior to Week 54, among the patients who used oral corticosteroids at baseline.2,6
Efficacy results with non-responder imputation for UC: At Week 54, 53% of patients achieved clinical remission vs. 45% at Week 102. Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement was achieved at Week 54 in 44% vs. 41% at Week 102. Corticosteroid-free remission was achieved at Week 54 by 46% vs. 37% at Week 102.2,6
Limitations: In an open-label extension, there is a potential for enrichment of the long-term data in the remaining patient populations, since patients who are unable to tolerate or do not respond to the drug often drop out. In the as-observed analysis, missing visit data were excluded, potentially increasing the percentage of responders.2,6
CD, Crohn's Disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IFX, infliximab; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous; SES-CD, Simplified Endoscopic Activity Score for Crohn's Disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038 5. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Supplementary material to: Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 6. Hanauer SB, Sand BE, Schreiber S, et al. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: two randomized phase 3 trials (LIBERTY). Gastroenterol. 2024;167(5):919-933. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.006
Post hoc analysis: LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC4
Remission rates—ZYMFENTRA with and without immunosuppressants4
A post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies evaluated ZYMFENTRA in patients receiving monotherapy or combination therapy with immunosuppressants.
Clinical remission
Primary endpoint
After IFX IV induction, patients achieved clinical remission at Week 54 and maintained clinical remission at Week 102.4
Study limitations4
- Despite the longer follow-up period and larger sample size relative to previous studies, larger, longer-term, monotherapy versus combination therapy studies are warranted to further evaluate safety and to elucidate the impact of ADA formation and PK level on efficacy over longer-term maintenance exposure
- Due to the exploratory nature of post hoc analyses, the studies were not powered to show a difference between monotherapy and combination therapy
- Concomitant treatment with immunosuppressants in the LIBERTY studies was dependent on patients having previously received stable doses of immunosuppressants (ie, patients were not randomized to receive immunosuppressants), thus only permitting indirect conclusions
- The majority of patients in the combination therapy group received thiopurine, limiting the generalization of the findings to combination therapy with other immunosuppressants. However, an earlier study found no difference between MTX and AZA in reducing ADA formation associated with IFX treatment
Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab by baseline immunosuppressant use4,5
Study Note: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=192) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Co-primary endpoints were clinical remission and endoscopic response. Secondary endpoints included endoscopic remission and corticosteroid-free remission.4,5
Study Note: All-randomized population (N=192) treated in the extension phase. Includes all patients randomly assigned to the ZYMFENTRA SC arm at Week 10 and who were treated in the extension phase. Patients with dose escalation to ZYMFENTRA SC 240 mg prior to the scheduled visit of interest were considered non-remitters or non-responders for efficacy outcomes. Efficacy endpoints were compared between monotherapy and combination therapy groups using the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test, stratified by factors used for randomization. All comparisons were P≥0.05.4,5
Definition of endpoints: clinical remission (CDAI score <150); endoscopic response: 50% decrease from baseline in SES-CD score; clinical response (CDAI-100 response [decrease in CDAI score of ≥100 points from baseline]); endoscopic remission (SES-CD score of ≤4 [with a decrease from baseline of ≥2 points] with all subscores ≤1); corticosteroid-free remission (CDAI score <150 without receiving any corticosteroids for ≥8 weeks prior to the scheduled visit of interest [evaluated among patients who were using oral corticosteroids at baseline]); deep remission (Meeting both clinical remission and endoscopic remission criteria).4,5
ADA, antidrug antibody; AZA, azathioprine; CD, Crohn's disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IFX, infliximab; IV, intravenous; mMS, modified Mayo Score; MTX, methotrexate; PK, pharmacokinetics; SC, subcutaneous; SES-CD, Simplified Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038 5. Hanauer SB, Sand BE, Schreiber S, et al. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: two randomized phase 3 trials (LIBERTY). Gastroenterol. 2024;167(5):919-933. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.006
Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab by baseline immunosuppressant use4,5
Study Note: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study (N=237) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZYMFENTRA as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC. Primary endpoint was clinical remission. Secondary endpoints were clinical response, histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement, and corticosteroid-free remission.4,5
Study Note: All-randomized population (N=237) treated in the extension phase. Includes all patients randomly assigned to the ZYMFENTRA SC arm at Week 10 and who were treated in the extension phase. Patients with dose escalation to ZYMFENTRA SC 240 mg prior to the scheduled visit of interest were considered non-remitters or non-responders for efficacy outcomes. Efficacy endpoints were compared between monotherapy and combination therapy groups using the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test, stratified by factors used for randomization. All comparisons were P≥0.05.4,5
Definition of endpoints: clinical remission (Modified Mayo score [SF and endoscopic subscores of 0 or 1, rectal bleeding subscore of 0]); clinical response (Decrease from baseline in modified Mayo score of ≥2 points and ≥30% [alongside decrease of ≥1 point or absolute score of 0/1 in rectal bleeding subscore]); endoscopic-histologic mucosal improvement (Absolute endoscopic subscore of 0/1 [modified Mayo score] and absolute Robarts Histopathology Index score of ≤3 points [alongside lamina propria neutrophils and neutrophils in epithelium subscore of 0]); corticosteroid-free remission (Based on modified Mayo score without receiving any corticosteroids for ≥8 weeks prior to the scheduled visit of interest).4,5
ADA, antidrug antibody; AZA, azathioprine; CD, Crohn's disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IFX, infliximab; IV, intravenous; mMS, modified Mayo Score; MTX, methotrexate; PK, pharmacokinetics; SC, subcutaneous; SES-CD, Simplified Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038 5. Hanauer SB, Sand BE, Schreiber S, et al. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: two randomized phase 3 trials (LIBERTY). Gastroenterol. 2024;167(5):919-933. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.05.006
Real-world study of IFX SC serum concentration thresholds associated with therapeutic outcomes5
Percentage of patients with IFX SC concentration thresholds associated with therapeutic outcomes5
Serum IFX SC concentration according to study outcomes5
Study Note:
- The cross-sectional study included 71 adults with IBD treated with subcutaneous infliximab [SC-IFX] concentrations at a maintenance dose of 120 mg/2 weeks5
- The primary therapeutic outcomes included sustained clinical remission; composite clinical and biomarker remission (clinical remission and C-reactive protein <5 mg/L); biochemical remission (fecal calprotectin <250 μg/g); and deep remission (clinical, biomarker, and biochemical remission)5
IFX SC concentration was the only variable independently associated with the investigated outcomes. Notably, the use of immunomodulators and the IFX IV regimen used before the shift did not influence the therapeutic outcomes studied.5
Current evidence does not establish a direct correlation between the pharmacokinetic attributes of ZYMFENTRA and its clinical efficacy. The prognostic relevance of serum drug concentrations should be interpreted within the complete clinical context, not as the sole predictor of therapeutic outcomes.5
Study limitations included: small sample size, lack of endoscopic data, use of a drug-sensitive assay for measuring antibodies to IFX, IFX SC concentrations >20 μg/mL could not be measured, mucosal healing could not be directly measured, excluded patients with a BMI >30, and only an association of high drug concentration with better outcomes could be established.5
BMI, body mass index; CD, Crohn's disease; CDAI, Crohn's Disease Activity Index; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; IFX, infliximab; IV, intravenous; SC, subcutaneous; UC, ulcerative colitis.
References: 1. ZYMFENTRA Prescribing Information. Celltrion USA, Inc. 2024. 2. Colombel J-F, Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S. Subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) as maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: 2-year results from open-label extensions of two randomized controlled trials (LIBERTY). J Crohns Colitis. 2025;19(6):1-15. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf060 3. Schreiber S, Ben-Horin S, Leszczyszyn J, et al. Randomized controlled trial: subcutaneous vs intravenous infliximab CT-P13 maintenance in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. 2021;160(7):2340-2353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.068 4. Schreiber S, Colombel J-F, Hanauer SB. Comparing outcomes with subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) by baseline immunosuppressant use: a post hoc analysis of the LIBERTY-CD and LIBERTY-UC studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Published online April 30, 2025. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaf038 5. Roblin X, Nancey S, Papamichael K, et al. Higher serum infliximab concentrations following subcutaneous dosing are associated with deep remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2024;18(5):679-685. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad188
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS and MALIGNANCY
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with TNF blockers, including ZYMFENTRA, are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Discontinue ZYMFENTRA if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis, including reactivation of latent tuberculosis. Patients with tuberculosis have frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Test patients for latent tuberculosis before ZYMFENTRA use and during therapy. Initiate treatment for latent infection prior to ZYMFENTRA use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and pneumocystosis. Patients with histoplasmosis or other invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Antigen and antibody testing for histoplasmosis may be negative in some patients with active infection. Consider empiric anti-fungal therapy in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella and Listeria.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with ZYMFENTRA, including the possible development of tuberculosis in patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy.
MALIGNANCY
Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, including infliximab products.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including infliximab products. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. Almost all patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. The majority of reported cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis and most were in young adult males.
Contraindications
- ZYMFENTRA is contraindicated in patients with a history of a severe hypersensitivity reaction to infliximab-dyyb, other infliximab products, any of the inactive ingredients in ZYMFENTRA, or any murine proteins. Reactions have included anaphylaxis.
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious infections: Avoid in patients with active infection. If infection develops, conduct a prompt/complete diagnostic workup appropriate for immunocompromised patients and initiate antimicrobials. If systemic illness develops in patients who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic, consider empiric antifungals.
- Malignancies: Malignancies, including lymphoma, were greater in TNF-blocker-treated patients. Consider the higher risk of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) with combination therapy versus increased risk of immunogenicity and hypersensitivity reactions with monotherapy.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation: Test for HBV infection before starting treatment. Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy for active HBV infection. If reactivation occurs, stop ZYMFENTRA and begin anti-viral therapy.
- Hepatotoxicity: Severe hepatic reactions, some fatal or necessitating liver transplantation have occurred in patients receiving infliximab products. Monitor hepatic enzymes and liver function tests every 3-4 months during treatment; investigate liver enzyme elevations and interrupt treatment if drug-induced liver injury is suspected. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop.
- Congestive heart failure (CHF): New onset or worsening symptoms may occur. Avoid in patients with CHF. Monitor for new/worsening symptoms when administering ZYMFENTRA.
- Hematologic reactions: Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if signs and symptoms of cytopenia develop; consider stopping if significant hematologic abnormalities develop.
- Hypersensitivity and other administration reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis have occurred with intravenous formulations of infliximab; discontinue ZYMFENTRA and start appropriate therapy.
- Neurologic reactions: Exacerbation or new onset CNS demyelinating disorders may occur; consider discontinuation of ZYMFENTRA.
- Risk of infection with concurrent administration of other biological products: Concurrent use with other immunosuppressive biologics may increase risk of infection.
- Risk of additive immunosuppressive effects from prior biological products: Consider the half-life and mode of action of prior biologics.
- Autoimmunity: Formation of autoantibodies and development of lupus-like syndrome may occur; discontinue ZYMFENTRA if symptoms develop.
- Vaccinations and use of live vaccines/therapeutic infectious agents: Prior to initiating ZYMFENTRA bring patients up to date with vaccinations. Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with ZYMFENTRA. A 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of live vaccines to infants exposed in utero to infliximab.
Common Adverse Reactions (≥3%)
- Ulcerative Colitis: COVID-19, anemia, arthralgia, injection site reaction, increased alanine aminotransferase, and abdominal pain.
- Crohn's Disease: COVID-19, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, injection site reaction, diarrhea, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, arthralgia, increased alanine aminotransferase, hypertension, urinary tract infection, neutropenia, dizziness, and leukopenia.
Drug Interactions
- Concurrent use with immunosuppressive biologics used to treat UC and CD is not recommended due to risk of infection.
- Formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased levels of cytokines during chronic inflammation. ZYMFENTRA could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes potentially resulting in decreased exposure of CYP450 substrates and requiring dose adjustments.
INDICATIONS
Crohn's Disease
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn's disease following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
Ulcerative Colitis
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING.
INDICATIONS
Crohn's Disease
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn's disease following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
Ulcerative Colitis
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS and MALIGNANCY
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with TNF blockers, including ZYMFENTRA, are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Discontinue ZYMFENTRA if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis, including reactivation of latent tuberculosis. Patients with tuberculosis have frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Test patients for latent tuberculosis before ZYMFENTRA use and during therapy. Initiate treatment for latent infection prior to ZYMFENTRA use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and pneumocystosis. Patients with histoplasmosis or other invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Antigen and antibody testing for histoplasmosis may be negative in some patients with active infection. Consider empiric anti-fungal therapy in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella and Listeria.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with ZYMFENTRA, including the possible development of tuberculosis in patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy.
MALIGNANCY
Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, including infliximab products.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including infliximab products. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. Almost all patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. The majority of reported cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis and most were in young adult males.
Contraindications
- ZYMFENTRA is contraindicated in patients with a history of a severe hypersensitivity reaction to infliximab-dyyb, other infliximab products, any of the inactive ingredients in ZYMFENTRA, or any murine proteins. Reactions have included anaphylaxis.
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious infections: Avoid in patients with active infection. If infection develops, conduct a prompt/complete diagnostic workup appropriate for immunocompromised patients and initiate antimicrobials. If systemic illness develops in patients who reside or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic, consider empiric antifungals.
- Malignancies: Malignancies, including lymphoma, were greater in TNF-blocker-treated patients. Consider the higher risk of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) with combination therapy versus increased risk of immunogenicity and hypersensitivity reactions with monotherapy.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation: Test for HBV infection before starting treatment. Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy for active HBV infection. If reactivation occurs, stop ZYMFENTRA and begin anti-viral therapy.
- Hepatotoxicity: Severe hepatic reactions, some fatal or necessitating liver transplantation have occurred in patients receiving infliximab products. Monitor hepatic enzymes and liver function tests every 3-4 months during treatment; investigate liver enzyme elevations and interrupt treatment if drug-induced liver injury is suspected. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms develop.
- Congestive heart failure (CHF): New onset or worsening symptoms may occur. Avoid in patients with CHF. Monitor for new/worsening symptoms when administering ZYMFENTRA.
- Hematologic reactions: Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if signs and symptoms of cytopenia develop; consider stopping if significant hematologic abnormalities develop.
- Hypersensitivity and other administration reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis have occurred with intravenous formulations of infliximab; discontinue ZYMFENTRA and start appropriate therapy.
- Neurologic reactions: Exacerbation or new onset CNS demyelinating disorders may occur; consider discontinuation of ZYMFENTRA.
- Risk of infection with concurrent administration of other biological products: Concurrent use with other immunosuppressive biologics may increase risk of infection.
- Risk of additive immunosuppressive effects from prior biological products: Consider the half-life and mode of action of prior biologics.
- Autoimmunity: Formation of autoantibodies and development of lupus-like syndrome may occur; discontinue ZYMFENTRA if symptoms develop.
- Vaccinations and use of live vaccines/therapeutic infectious agents: Prior to initiating ZYMFENTRA bring patients up to date with vaccinations. Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with ZYMFENTRA. A 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of live vaccines to infants exposed in utero to infliximab.
Common Adverse Reactions (≥3%)
- Ulcerative Colitis: COVID-19, anemia, arthralgia, injection site reaction, increased alanine aminotransferase, and abdominal pain.
- Crohn's Disease: COVID-19, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, injection site reaction, diarrhea, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, arthralgia, increased alanine aminotransferase, hypertension, urinary tract infection, neutropenia, dizziness, and leukopenia.
Drug Interactions
- Concurrent use with immunosuppressive biologics used to treat UC and CD is not recommended due to risk of infection.
- Formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased levels of cytokines during chronic inflammation. ZYMFENTRA could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes potentially resulting in decreased exposure of CYP450 substrates and requiring dose adjustments.
INDICATIONS
Crohn's Disease
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn's disease following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
Ulcerative Colitis
- ZYMFENTRA is indicated in adults for maintenance treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis following treatment with an infliximab product administered intravenously.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING.
